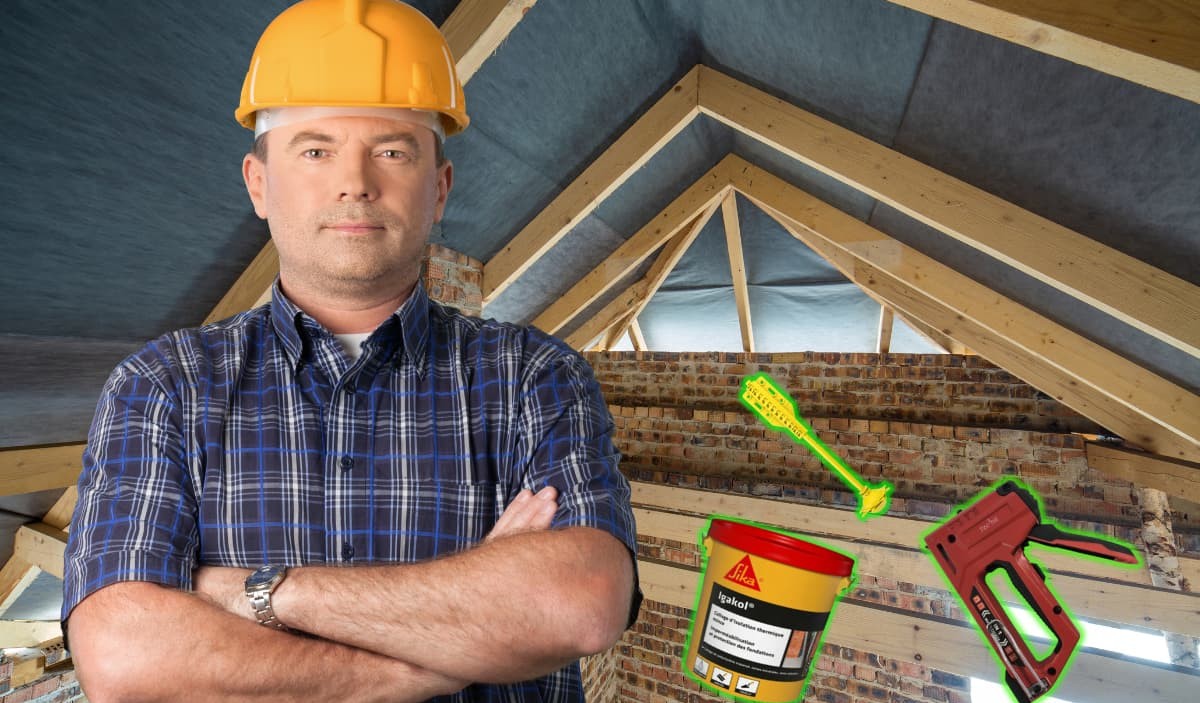
Glass wool is one of the most widespread and easy-to-install materials for insulating walls and attics. On roofs in particular, it is simply laid between the rafters. While glass wool's natural elasticity enables it to fill the space and virtually hold its own between two rafters, it is often preferable to fix it in place to ensure that it doesn't fall out in the medium or long term.
Craftsmen and do-it-yourselfers use a number of equally effective techniques to ensure proper fixing. In this article, we present 5 techniques for fixing glass wool between rafters.
Stapling glass wool
The stapling technique for fixing glass wool is distinguished by its simplicity and practical effectiveness. This method involves using metal staples to fasten insulation directly to wooden structures, such as rafters.
Staples
The staples used must be corrosion-resistant and strong enough to hold the glass wool in place. Typically, stainless steel or galvanized staples are recommended for their durability and resistance to moisture. Their length is also important and should be chosen according to the thickness of the glass wool, with a generally recommended minimum length of around 12 mm.
Staple spacing is another important aspect. Optimum staple density is required to ensure secure attachment of the glass wool. The staples must be placed at regular intervals, generally every 150 to 300 mm, to avoid sagging or movement of the insulation.
Hanger installation
Using hangers to fix glass wool is an advanced method that combines mechanics and precision to ensure effective, long-lasting insulation.
These hangers, designed specifically for glass wool insulation, attach directly to the rafters. Their unique design distributes the weight of the insulation evenly, reducing the risk of sagging over time.
They offer more secure and stable fastening than traditional methods, thanks in particular to their ability to adapt to different insulation thicknesses and their resistance to variations in temperature and humidity.
What's more, these hangers are often designed to facilitate installation, allowing precise adjustment of the insulation position and ensuring a solid connection with the building structure. As well as improving the longevity of the insulation, this method also helps maintain its thermal efficiency by avoiding thermal bridges and displacements that could compromise the insulation.
Fixing clips for glass wool
The use of glass wool clips is an efficient and precise method, based on mechanical principles to ensure optimum insulation.
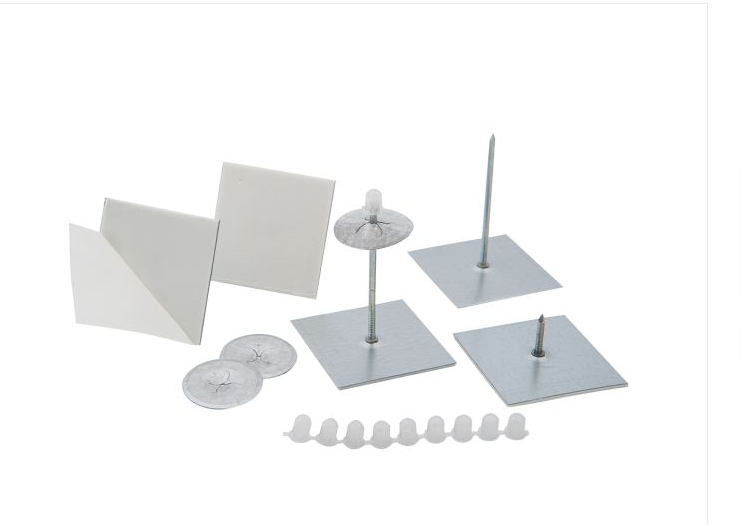
These clips, specially designed for glass wool installation, are fastened to the rafters at intervals calculated to distribute the holding force evenly. Typically, these clips are spaced 400 to 600 mm along the rafters to ensure adequate support for the insulation, minimizing the risk of warping or sagging.
The design of these clips makes installation quick and easy, while ensuring a firm grip on the building structure.
What's more, the mechanical strength of these clips is designed to support the weight of the glass wool without flexing, maintaining the integrity and thermal efficiency of the insulation over the long term. These clips, often made from corrosion-resistant materials such as galvanized steel, ensure greater durability even in environments exposed to humidity.
Cleats or battens to fix glass wool between rafters
Using cleats or battens to fix the glass wool between the rafters is a method that combines robustness and precision. This technique involves positioning pieces of wood horizontally on the rafters, gripping the glass wool for optimum hold.
The cleats or battens are usually spaced strategically, often every 40 to 60 cm, to create a support structure that prevents glass wool sagging and ensures even distribution of the insulation. This approach has the advantage of adding a layer of structural stability, strengthening the overall installation.
In addition, by creating an air space between the insulation and the interior cladding, cleats or battens improve thermal efficiency by minimizing thermal bridges. The materials used for these battens, such as treated wood or composite, offer resistance to humidity and temperature variations, contributing to the longevity of the installation.
Glass wool adhesive
The use of specific adhesives for fixing glass wool is a targeted method based on precise chemical and physical characteristics. These adhesives, often based on polymers such as polyurethane or acrylic, must have a strong adhesion, with a load-bearing capacity of up to 100-200 kg/m², to guarantee solid attachment of glass wool to structures such as rafters.
Quantitatively, the adhesive is applied sparingly, using around 20-40 grams per square meter of insulation, although this may vary according to product specificity. These adhesives are designed to withstand temperature variations ranging from -40°C to +80°C, making them suitable for a variety of construction environments.
Glue setting, a crucial factor, usually takes place within 10 to 30 minutes, providing sufficient working time to adjust the insulation before final fixing. Long-term durability is ensured by high resistance to moisture and chemical agents, preventing glass wool from degrading and compromising its insulating properties.

Julien G.
Juliena mechanical engineering graduate and specialist in climate engineering since 2009, has become a writer specializing in renewable energies, with expertise in heat pumps and photovoltaic solar panels for individual housing.
See all articles by this author






